Introduction
Hello readers! Welcome to this comprehensive article on the advantages and disadvantages of Customer Relationship Management (CRM). In today's highly competitive business landscape, organizations strive to establish and maintain strong relationships with their customers. CRM is a powerful tool that enables businesses to effectively manage and enhance these relationships, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. However, like any other business strategy, CRM also has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will explore these aspects in detail, providing you with valuable insights to make informed decisions for your organization's CRM implementation.
Advantages of CRM
🔹 Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: CRM allows businesses to better understand their customers' needs and preferences, enabling personalized interactions and tailored solutions. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
🔹 Improved Customer Retention: By effectively managing customer interactions and providing exceptional service, CRM helps businesses retain their existing customers. This reduces customer churn and increases revenue through long-term relationships.
🔹 Streamlined Sales Process: CRM systems provide sales teams with valuable insights and data, enabling them to prioritize leads, track sales activities, and streamline the sales process. This enhances efficiency and productivity.
🔹 Efficient Marketing Campaigns: CRM enables businesses to segment their customer base, target specific groups, and personalize marketing campaigns. This leads to higher response rates and improved marketing ROI.
🔹 Effective Communication: CRM systems centralize customer data, facilitating seamless communication across departments. This ensures consistent and coordinated interactions, minimizing misunderstandings and enhancing collaboration.
🔹 Data-Driven Decision Making: With CRM, businesses can access real-time data and generate insightful reports. This helps in making data-driven decisions, identifying trends, and forecasting future customer behavior.
🔹 Competitive Advantage: By leveraging CRM tools and strategies, businesses gain a competitive edge in the market. CRM enables organizations to differentiate themselves by delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
CRM plays a crucial role in enhancing customer satisfaction by enabling businesses to gain a deeper understanding of their customers. By collecting and analyzing customer data, companies can identify their preferences, behaviors, and pain points. This valuable information allows businesses to tailor their products, services, and interactions to meet specific customer needs.
Personalization is a key element of enhanced customer satisfaction. With a robust CRM system, businesses can create highly personalized experiences for their customers. By utilizing the data collected in CRM, companies can provide tailored recommendations, customized offers, and personalized communication. This level of personalization makes customers feel valued and understood, leading to increased satisfaction and loyalty.
Moreover, CRM enables businesses to provide exceptional customer service. By centralizing customer data and interaction history, CRM systems empower customer service representatives to deliver timely and relevant support. Quick access to customer information allows representatives to address issues more efficiently, resulting in faster resolution and higher customer satisfaction.
Improved Customer Retention
Customer retention is a vital aspect of any successful business. CRM helps businesses effectively manage their customer relationships, leading to improved customer retention rates. By tracking customer interactions, preferences, and purchase history, CRM systems enable companies to identify opportunities for upselling, cross-selling, and repeat purchases.
CRM also facilitates proactive customer engagement. Through automated reminders and notifications, businesses can reach out to customers at the right time, offering personalized recommendations or exclusive deals. This proactive approach strengthens the customer relationship and increases the likelihood of repeat purchases.
Additionally, CRM systems enable businesses to provide loyalty programs and rewards to their customers. By tracking customer activities and spending patterns, businesses can offer targeted rewards and incentives, fostering customer loyalty and encouraging repeat business.
Streamlined Sales Process
CRM systems are invaluable tools for sales teams. They provide comprehensive insights into customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history, enabling sales representatives to prioritize leads and opportunities effectively. By segmenting customers based on their buying potential, sales teams can focus their efforts on high-value prospects, resulting in a more streamlined and efficient sales process.
CRM also facilitates sales pipeline management. With a CRM system, sales representatives can track the progress of each deal, from the initial lead to the final sale. This helps identify potential bottlenecks or areas for improvement in the sales process, allowing businesses to make necessary adjustments and optimize their sales strategies.
Furthermore, CRM systems enable sales teams to collaborate and share information seamlessly. By centralizing customer data, CRM systems eliminate silos and ensure that all relevant information is accessible to the entire sales team. This promotes collaboration, reduces duplication of efforts, and enhances overall sales performance.
Efficient Marketing Campaigns
CRM is a valuable tool for marketing teams, enabling them to create and execute efficient and targeted marketing campaigns. By segmenting their customer base based on demographics, preferences, and purchase history, businesses can deliver personalized marketing messages to specific groups of customers.
CRM systems provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, allowing businesses to identify trends and patterns. This information helps marketing teams develop more effective marketing strategies and campaigns that resonate with their target audience.
Moreover, CRM systems enable businesses to track and measure the success of their marketing campaigns. By analyzing customer responses and conversion rates, companies can determine the ROI of their marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions on future marketing investments.
Effective Communication
One of the key advantages of CRM is its ability to facilitate effective communication within an organization. By centralizing customer data and interaction history, CRM systems ensure that all departments have access to the same up-to-date information. This eliminates the need for multiple data sources and reduces the risk of miscommunication or conflicting information.
CRM systems enable seamless collaboration between departments, such as sales, marketing, and customer service. With a shared view of customer data, teams can work together to provide a consistent and coordinated customer experience. For example, if a customer reaches out to customer service with a specific issue, the representative can quickly access the customer's purchase history and preferences from CRM, enabling them to provide relevant and personalized support.
Furthermore, CRM systems facilitate efficient communication with customers. By utilizing CRM tools such as automated email marketing or personalized messaging, businesses can reach out to customers with relevant information, updates, or offers. This helps maintain regular communication and fosters stronger relationships with customers.
Data-Driven Decision Making
CRM systems provide businesses with valuable insights and data that can be utilized for data-driven decision making. By analyzing customer data, businesses can identify trends, patterns, and correlations that can inform strategic decisions.
CRM systems enable businesses to generate comprehensive reports and analytics on customer behavior, sales performance, marketing effectiveness, and more. These reports provide actionable insights for business leaders, allowing them to make informed decisions that drive growth and success.
Moreover, CRM systems support forecasting and predictive analytics. By analyzing historical data and customer trends, businesses can make accurate predictions about future customer behavior and market trends. This helps in planning and strategizing for the future and staying ahead of the competition.
Competitive Advantage
In today's highly competitive business landscape, CRM can provide a significant competitive advantage. By delivering exceptional customer experiences and building strong customer relationships, businesses can differentiate themselves from their competitors.
CRM enables businesses to provide personalized interactions and tailored solutions, creating a unique and memorable customer experience. This level of personalization sets businesses apart and helps in building long-term customer loyalty.
Furthermore, CRM systems empower businesses with valuable customer insights that can be used to identify market trends and customer preferences. By staying ahead of the curve and adapting to changing customer needs, businesses can gain a competitive edge and establish themselves as industry leaders.
Moreover, businesses that effectively utilize CRM systems can optimize their sales and marketing efforts, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. By streamlining processes and focusing on high-value opportunities, businesses can outperform their competitors and achieve higher revenue growth.
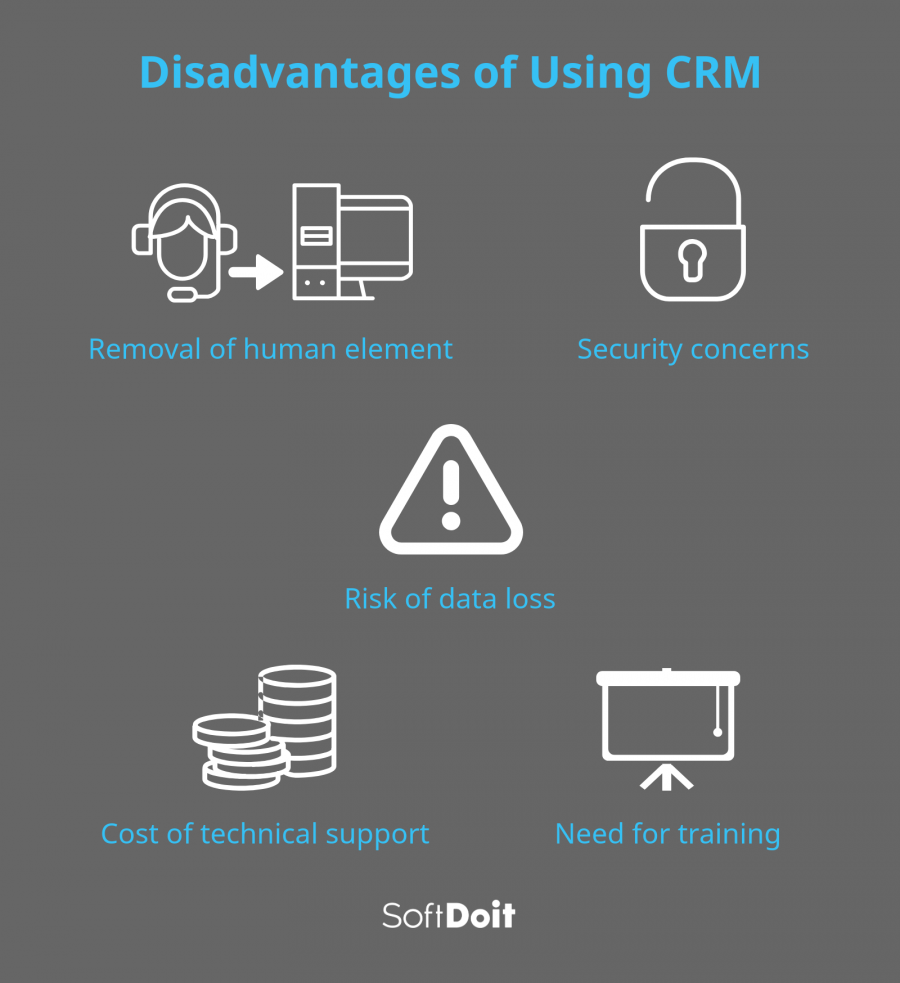
Disadvantages of CRM
🔹 Implementation Challenges: Implementing a CRM system can be complex and time-consuming. It requires significant planning, resource allocation, and employee training. Poor implementation can lead to resistance and limited adoption.
🔹 Costly Investment: CRM implementation involves financial investments in software, infrastructure, customization, and maintenance. Small businesses with limited budgets may find it challenging to afford a robust CRM solution.
🔹 Data Security Risks: Centralized customer data in CRM systems poses potential security risks. Breaches or unauthorized access can lead to the compromise of sensitive customer information, damaging the organization's reputation.
🔹 Integration Issues: Integrating CRM systems with existing software and databases can be complex. Incompatibilities and data migration challenges may arise, leading to disruptions in business operations.
🔹 Training and User Adoption: Proper training and user adoption are critical for successful CRM implementation. Resistance to change and lack of user acceptance can hinder the system's effectiveness and ROI.
🔹 Overreliance on Technology: While CRM systems provide valuable insights and automation, overreliance on technology can lead to depersonalized customer interactions. Businesses must strike a balance between automation and human touch.
🔹 Evolving Customer Expectations: Customer expectations are constantly evolving. CRM systems need to adapt and keep pace with changing customer preferences and emerging technologies.
Implementation Challenges
Implementing a CRM system
Implementation Challenges
Implementing a CRM system can be a complex and challenging process for businesses. There are several common implementation challenges that organizations may face when adopting CRM:
1. Lack of Proper Planning
One of the primary challenges in CRM implementation is the lack of proper planning. Organizations need to have a clear understanding of their objectives, requirements, and desired outcomes before embarking on the CRM implementation journey. Without a well-defined plan, businesses may struggle to align the CRM system with their specific needs and goals, leading to inefficiencies and limited adoption.
2. Resource Allocation
Implementing a CRM system requires dedicated resources, including financial, technological, and human resources. Organizations need to allocate sufficient funds and budget for the CRM software, hardware, infrastructure, and customization. Additionally, they need to invest in training and development programs to ensure that employees are equipped with the necessary skills to effectively use the CRM system.
3. Employee Resistance
Resistance to change is a common challenge in CRM implementation. Employees may be hesitant or resistant to adopting new technologies or processes, especially if they perceive it as a threat to their existing roles or routines. To address this challenge, organizations need to communicate the benefits of CRM to employees, involve them in the decision-making process, and provide comprehensive training and support to facilitate a smooth transition.
4. Data Quality and Migration
Data quality and migration are critical aspects of CRM implementation. Organizations need to ensure that the existing data is accurate, complete, and of high quality before migrating it to the CRM system. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights and hinder the effectiveness of the CRM system. Additionally, data migration can be a complex process, especially when integrating multiple data sources or legacy systems. Careful planning and testing are required to ensure a seamless and error-free data migration process.
5. Customization and Integration
Each organization has unique processes, workflows, and requirements. Therefore, customization and integration are crucial to align the CRM system with the specific needs of the business. Organizations may face challenges in customizing the CRM system to match their existing processes and integrating it with other software or databases. Incompatibilities, data mapping issues, and technical complexities can arise, requiring careful planning and collaboration with IT teams or external consultants.
6. User Adoption and Training
Successful CRM implementation relies on user adoption and utilization of the system. However, employees may struggle to understand the functionalities and benefits of the CRM system without proper training and support. Organizations need to invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that employees are proficient in using the CRM system and understand its value. Ongoing support and regular communication are also important to address any challenges or questions that users may have.
7. Scalability and Future Growth
Organizations need to consider the scalability and future growth potential of the CRM system during implementation. As businesses evolve and expand, the CRM system should be able to accommodate increasing volumes of data, users, and functionalities. Scalability ensures that the CRM system can grow with the organization without requiring significant reimplementation or system upgrades.
Costly Investment
Implementing a CRM system involves financial investments that can vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization. The costs associated with CRM implementation can include:
1. Software Costs
The cost of CRM software can vary based on factors such as the vendor, the features and functionalities included, and the licensing model (e.g., subscription-based or perpetual license). Organizations need to carefully evaluate different CRM software options and choose the one that best fits their budget and requirements.
2. Infrastructure Costs
In addition to the software costs, organizations need to consider the infrastructure required to support the CRM system. This includes hardware, servers, networking equipment, and storage devices. Cloud-based CRM solutions can help reduce infrastructure costs as they rely on the vendor's infrastructure instead of requiring on-premises hardware.
3. Customization and Integration Costs
Customizing and integrating the CRM system to match the organization's specific needs can also incur additional costs. This includes hiring developers or consultants to customize the CRM software, integrate it with existing systems, and ensure data consistency and integrity.
4. Training and Support Costs
Proper training and ongoing support are essential for successful CRM implementation. Organizations need to allocate resources for training programs, user documentation, and support channels such as help desks or dedicated CRM support teams. These costs ensure that employees are proficient in using the CRM system and can effectively leverage its features and functionalities.
5. Maintenance and Upgrades
CRM systems require regular maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance and security. Organizations need to consider the costs associated with system updates, bug fixes, and technical support. Additionally, as the CRM system evolves and new versions are released, organizations may need to invest in system upgrades to access the latest features and enhancements.
6. Total Cost of Ownership
When evaluating the cost of CRM implementation, organizations must consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). TCO includes not only the initial implementation costs but also the ongoing costs such as licensing fees, maintenance, upgrades, and training. Calculating the TCO helps organizations make informed decisions about the long-term financial implications of CRM implementation.
Data Security Risks
While CRM systems offer numerous benefits, they also introduce potential data security risks that organizations need to be aware of:
1. Unauthorized Access
Centralizing customer data in a CRM system makes it a valuable target for unauthorized access. Hackers or malicious actors may attempt to gain access to the CRM system to steal sensitive customer information, such as personal details, financial data, or confidential business information. Organizations need to implement robust security measures, such as secure authentication protocols, encryption, and access controls, to protect against unauthorized access.
2. Data Breaches
Data breaches can occur when customer data stored in a CRM system is accessed or compromised without authorization. Breaches can result from external attacks, insider threats, or human errors such as lost or stolen devices. Organizations need to implement strong security measures, regularly evaluate and update their security protocols, and educate employees on data protection best practices to mitigate the risk of data breaches.
3. Compliance Violations
Depending on the industry and geographic location, organizations may be subject to various data protection and privacy regulations. CRM systems must comply with these regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and damage to the organization's reputation. Organizations need to ensure that their CRM systems adhere to relevant data protection and privacy requirements.
4. Insider Threats
Insider threats pose a significant risk to data security. Employees with authorized access to the CRM system may intentionally or unintentionally misuse or disclose customer data. Organizations need to implement strict access controls, monitor user activities, and provide regular security awareness training to employees to mitigate the risk of insider threats.
5. Data Loss
Data loss can occur due to hardware failures, software errors, or natural disasters. Organizations need to implement robust data backup and disaster recovery strategies to ensure the availability and integrity of customer data stored in the CRM system. Regular backups, off-site storage, and testing of recovery procedures are essential to mitigate the risk of data loss.
6. Vendor Security
When selecting a CRM vendor, organizations need to evaluate the vendor's security practices and protocols. This includes assessing the vendor's data protection measures, certifications, and compliance with industry standards. A reputable CRM vendor should have robust security measures in place to protect customer data and provide transparent information about their security practices.
Integration Issues
Integrating a CRM system with existing software, databases, and processes can present several challenges:
1. Compatibility and Incompatibility
Integrating a CRM system with existing software and databases requires compatibility between different systems. Incompatibilities can arise due to differences in data formats, protocols, or system requirements. Organizations need to carefully assess the compatibility of their existing systems with the CRM system and plan for any necessary data transformations or system modifications.
2. Data Migration
Data migration is a critical aspect of CRM integration. Transferring data from existing systems to the CRM system can be complex, especially when dealing with large volumes of data or multiple data sources. Organizations need to ensure that data is migrated accurately and without loss or corruption. Careful planning, data cleansing, and testing are essential to ensure a smooth data migration process.
3. Process Mapping and Redesign
Integrating a CRM system often requires organizations to map and redesign their existing processes to align with the capabilities and workflows of the CRM system. This can be a complex task that requires careful analysis of existing processes, identification of process gaps, and redesigning workflows to take full advantage of the CRM system's functionalities. Organizations need to involve key stakeholders and department representatives to ensure a comprehensive and successful process mapping and redesign process.
4. Training and User Adoption
Integrating a CRM system can introduce new processes and workflows for employees. This requires
4. Training and User Adoption
Integrating a CRM system can introduce new processes and workflows for employees. This requires proper training and support to ensure smooth user adoption. Employees need to understand how the CRM system integrates with their existing tools and workflows, and how it can enhance their productivity and efficiency. Training programs should be designed to address the specific needs of different user groups and provide hands-on experience to build confidence in using the integrated CRM system.
Organizations should also establish a support system to assist users during the transition and address any questions or issues that may arise. This can include providing a dedicated help desk, creating user manuals or documentation, and offering ongoing training and refresher sessions. User feedback and engagement should be actively encouraged to foster a culture of continuous improvement and utilization of the integrated CRM system.
5. Technical Challenges
Integrating a CRM system with existing software and databases can pose technical challenges. Differences in data structures, APIs, or protocols may require custom development or middleware solutions to enable seamless data flow between systems. Organizations need to involve IT teams or external consultants with expertise in CRM integration to address technical challenges effectively.
Testing and quality assurance are crucial during the integration process to ensure that all functionalities and data transfer processes are working as expected. Thorough testing should cover end-to-end scenarios, data integrity, and performance to identify and resolve any issues before going live with the integrated CRM system.
6. Scalability
Scalability is an important consideration when integrating a CRM system. Organizations need to assess the scalability of their existing systems and infrastructure to handle the increased data volumes and user load that come with CRM integration. This includes evaluating server capacities, network bandwidth, and storage capabilities to ensure that the integrated CRM system can accommodate future growth.
Cloud-based CRM solutions can provide scalability advantages as they can leverage the vendor's infrastructure to handle increased data and user demands. Organizations should consider the scalability features and options offered by CRM vendors when selecting an integrated CRM solution.
Training and User Adoption
Proper training and user adoption are critical for the success of CRM implementation. Organizations should focus on the following aspects to ensure effective training and user adoption:
1. Comprehensive Training Programs
Organizations should develop comprehensive training programs that cater to different user groups and roles within the organization. Training sessions should cover both the technical aspects of using the CRM system and the business processes and workflows that the CRM system supports. This can include hands-on exercises, role-playing scenarios, and real-life examples to make the training engaging and relevant to the users.
Training programs should be delivered through a variety of channels, including instructor-led sessions, online modules, and self-paced learning materials. This allows users to choose the most convenient and effective way to acquire the necessary skills and knowledge to use the CRM system effectively.
2. User Support and Documentation
In addition to training, organizations should provide ongoing user support and documentation to assist users in their day-to-day interactions with the CRM system. This can include user manuals, FAQs, knowledge bases, and dedicated help desks or support teams. Users should have easy access to resources that can help them troubleshoot issues, find answers to common questions, and learn about advanced features or functionalities.
Regular communication channels should also be established to provide updates, tips, and best practices related to the CRM system. This can be done through newsletters, intranet portals, or dedicated user forums. Encouraging user engagement and feedback helps create a collaborative environment where users can share their experiences and insights, fostering continuous learning and improvement.
3. Executive Support and Leadership
Executive support and leadership play a crucial role in driving user adoption of the CRM system. Leaders should actively communicate the importance and benefits of the CRM system to the organization and demonstrate their commitment to its successful implementation. This can be done through regular updates, town hall meetings, or internal communications that emphasize the value of the CRM system in achieving organizational goals.
Leaders should also lead by example and actively use the CRM system themselves. This sends a powerful message to employees about the importance of the CRM system and encourages them to embrace and utilize it in their daily work. Recognizing and rewarding employees who demonstrate proficiency in using the CRM system can further incentivize user adoption and create a positive culture around its utilization.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring and evaluating the usage and effectiveness of the CRM system is essential to identify areas for improvement and ensure ongoing user adoption. Organizations should establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of the CRM system on business objectives, such as increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, or enhanced marketing effectiveness.
User feedback and satisfaction surveys can provide valuable insights into how users perceive the CRM system and identify any pain points or areas that require further training or support. Usage analytics and data can also be analyzed to understand user behavior, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions to enhance user adoption and system utilization.
Regular reviews and updates of the training programs and support materials should be conducted to keep them aligned with the evolving needs of the organization and the CRM system. This ensures that users have access to up-to-date resources and continuous learning opportunities to maximize their proficiency and effectiveness in using the CRM system.
Overreliance on Technology
While CRM systems offer numerous benefits, organizations need to be cautious about overreliance on technology and ensure a balance between automation and human touch in customer interactions:
1. Depersonalization of Customer Interactions
CRM systems enable businesses to automate various aspects of customer interactions, such as email marketing, chatbots, or automated responses. While these automation features can improve efficiency and scalability, there is a risk of depersonalizing the customer experience. Customers may feel like they are interacting with a machine rather than a human, leading to a lack of emotional connection and reduced customer satisfaction.
Organizations should carefully consider which customer touchpoints can be automated without sacrificing the personalization and human touch that customers value. Balancing automation with personalized, human interactions can help foster stronger relationships and create memorable customer experiences.
2. Understanding Context and Nuance
CRM systems provide valuable customer data and insights, but they may not capture the full context and nuance of customer interactions. Understanding the context and individual preferences of customers often requires human judgment and empathy. Organizations should encourage their employees to actively listen to customers, ask probing questions, and adapt their approach based on the individual customer's needs and preferences.
While CRM systems can provide general guidelines or recommendations, employees should still have the flexibility to deviate from predefined scripts or workflows when necessary. Empowering employees to make judgment calls and personalize their interactions can lead to more meaningful and satisfying customer experiences.
3. Building Emotional Connections
Building emotional connections with customers is a crucial aspect of customer relationship management. CRM systems can provide insights into customer preferences and behaviors, but they may not capture the emotions or sentiments of customers. Emotional connections are often built through genuine human interactions, empathy, and understanding.
Organizations should train their employees to actively listen to customers, show empathy, and address their emotional needs. This can involve techniques such as active listening, paraphrasing, and responding with empathy. By combining the insights from the CRM system with human emotional intelligence, organizations can create deeper and more meaningful connections with their customers.
4. Continuous Evaluation and Adaptation
Organizations should continuously evaluate the effectiveness of their CRM system in balancing automation and human touch. This can be done through customer feedback, satisfaction surveys, and monitoring customer sentiment. If customers express dissatisfaction with automated interactions or lack of personalization, organizations should be open to adapting their approach and making necessary adjustments to meet customer expectations.
Regular training and development programs should be conducted to enhance employees' interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence. This helps employees develop the necessary skills to effectively connect with customers and provide personalized experiences, even in the context of CRM automation.
Evolving Customer Expectations
Customer expectations are constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing market dynamics, and shifting preferences. Organizations need to proactively address evolving customer expectations in their CRM strategies:
1. Agile and Adaptive CRM Systems
CRM systems should be designed to be agile and adaptable, allowing organizations to respond quickly to changing customer expectations. This can involve regular system updates and enhancements to introduce new features or functionalities that align with emerging customer needs.
Continuous monitoring of customer feedback, market trends, and competitor offerings can provide valuable insights into evolving customer expectations. Organizations should use these insights to inform their CRM strategies and make necessary adjustments to meet changing customer demands.
2. Personalized and Contextual Experiences
As customer expectations continue to evolve, there is a growing demand for personalized and contextual experiences. Organizations should leverage the insights and data available through their CRM systems to deliver tailored experiences to customers.
Personalized experiences can involve targeted marketing campaigns, customized product recommendations, or personalized customer support. By utilizing customer data and preferences, organizations can create experiences that resonate with individual customers and meet their unique needs.
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and chatbots are transforming customer interactions. Organizations should explore the integration of these technologies with their CRM systems to meet evolving customer expectations.
For
3. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and chatbots are transforming customer interactions. Organizations should explore the integration of these technologies with their CRM systems to meet evolving customer expectations.
For example, AI-powered chatbots can provide instant and personalized customer support, addressing common queries and issues in real-time. ML algorithms can analyze customer data to make intelligent recommendations or predictions, enhancing the personalization and relevance of customer interactions. By leveraging these technologies, organizations can deliver seamless and efficient customer experiences that align with evolving customer expectations.
4. Omnichannel Approach
Customers today expect a seamless experience across multiple channels and touchpoints. Organizations should adopt an omnichannel approach in their CRM strategies to meet these expectations. This involves integrating various customer touchpoints, such as social media, email, phone, and in-person interactions, into a cohesive and consistent customer journey.
CRM systems should enable organizations to track and manage customer interactions across different channels, ensuring that customers receive a consistent and personalized experience regardless of the channel they choose. This can involve integrating CRM with other systems such as marketing automation platforms, social media management tools, and customer support software to provide a unified view of customer interactions.
5. Proactive Engagement and Anticipation
Customers now expect organizations to anticipate their needs and proactively engage with them. CRM systems can play a vital role in enabling proactive engagement by providing insights into customer behavior and preferences.
By analyzing customer data, organizations can identify patterns, trends, and upcoming needs. For example, if a customer has a history of purchasing certain products, the CRM system can trigger automated recommendations or offers for related products. This proactive approach demonstrates that the organization understands and values the customer's needs, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6. Continuous Feedback and Improvement
To keep up with evolving customer expectations, organizations should seek continuous feedback from customers and use it to drive improvements in their CRM strategies. This can involve soliciting feedback through surveys, conducting focus groups, or analyzing customer reviews and social media sentiment.
Organizations should also regularly evaluate and update their CRM systems to incorporate new features, functionalities, and integrations that align with customer feedback and changing expectations. By actively listening to customers and making iterative improvements, organizations can stay ahead of the curve and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, CRM offers numerous advantages for businesses seeking to improve customer relationships, drive sales, and enhance marketing efforts. It enables personalized interactions, streamlines processes, and empowers data-driven decision-making. However, organizations must also be aware of the potential disadvantages and challenges associated with CRM implementation.
Implementing CRM requires careful planning, resource allocation, and training to overcome implementation challenges and ensure successful adoption. The costs associated with CRM implementation should be carefully evaluated, and organizations should prioritize data security measures to protect customer information.
Integration with existing systems, such as software and databases, may present challenges that require careful planning and collaboration. Training and user adoption are critical to maximizing the benefits of CRM, and organizations should focus on comprehensive training programs, ongoing user support, and continuous monitoring and evaluation.
It is important to strike a balance between automation and human touch to avoid depersonalizing customer interactions. Organizations should adapt their CRM strategies to meet evolving customer expectations by embracing emerging technologies, adopting an omnichannel approach, and proactively engaging with customers.
By addressing these considerations and continually evaluating and improving their CRM strategies, organizations can harness the full potential of CRM and gain a competitive edge in today's dynamic marketplace. Take action now and explore how CRM can transform your organization's customer relationships!
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only. The author and publisher are not liable for any losses or damages incurred as a result of implementing CRM strategies or technologies.
Post a Comment
Post a Comment