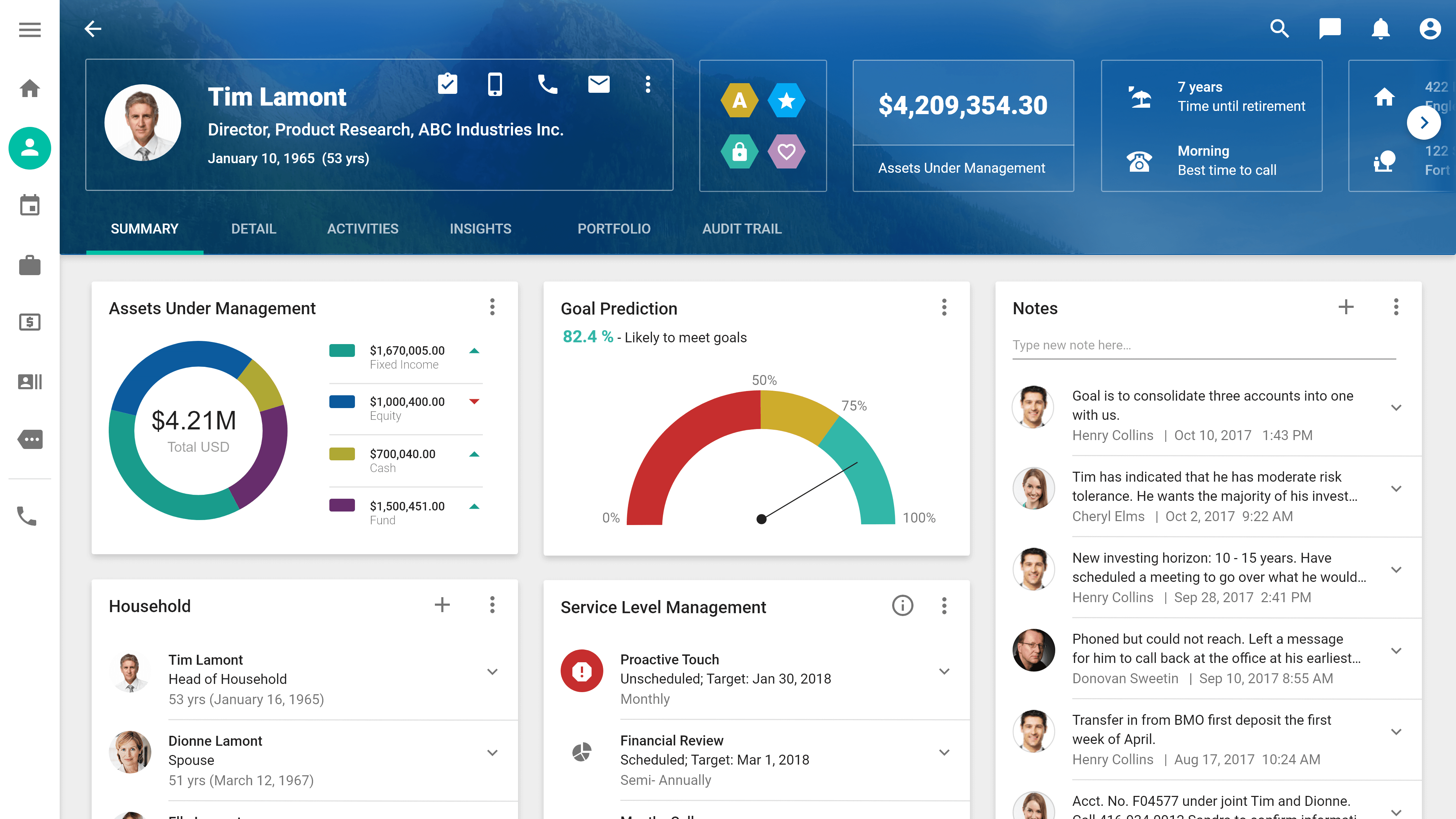
Introduction
Hello readers and welcome to this comprehensive article on financial services CRM software! In today's fast-paced and highly competitive business landscape, managing customer relationships efficiently is crucial for financial service providers. With the advent of CRM software, financial institutions have gained a powerful tool that helps streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive business growth. In this article, we will explore the strengths and weaknesses of financial services CRM software, its key features, and how it can benefit your organization.
Understanding Financial Services CRM Software
🔍 What is financial services CRM software?
Financial services CRM software is a specialized technology solution designed to assist financial institutions in managing their customer relationships effectively. It provides a centralized platform for capturing, analyzing, and utilizing customer data to drive personalized interactions and deliver exceptional service.
🔍 Why is CRM software crucial for financial services?
In the highly competitive financial services industry, building long-term relationships with clients is vital for success. CRM software enables financial institutions to gather valuable insights about their customers, track interactions, and tailor their offerings to meet individual needs. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also increases loyalty and boosts profitability.
🔍 How does financial services CRM software work?
Financial services CRM software integrates with various data sources within an organization, such as transactional systems, customer support platforms, and marketing databases. By collating information from these sources, CRM software creates a comprehensive view of each customer, enabling financial institutions to deliver personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns.
Strengths of Financial Services CRM Software
🌟 Enhanced Customer Engagement:
CRM software enables financial institutions to engage with customers through multiple channels, including phone calls, emails, social media, and live chats. This omnichannel approach allows for seamless interactions, ensuring customers feel valued and heard at every touchpoint.
🌟 Data Centralization:
One of the key strengths of CRM software is its ability to centralize customer data. All relevant information, including contact details, transaction history, and communication records, is stored in a single database. This allows for easy access and a holistic view of each customer, facilitating personalized interactions and targeted marketing efforts.
🌟 Streamlined Sales Process:
CRM software provides tools and features that help automate and streamline the sales process. From lead generation to deal closure, financial institutions can track and manage the entire sales pipeline efficiently. This leads to improved sales team productivity and increased revenue generation.
🌟 Customizable Dashboards and Reports:
CRM software offers customizable dashboards and reports that provide real-time insights into key performance metrics. Financial institutions can track sales progress, customer satisfaction levels, and marketing campaign outcomes, enabling data-driven decision-making and performance evaluation.
🌟 Compliance and Security:
Financial services CRM software is designed to comply with industry regulations and security standards. It ensures sensitive customer data is protected and provides audit trails for regulatory purposes. This helps financial institutions maintain trust and meet compliance requirements.
🌟 Workflow Automation:
CRM software automates various manual tasks, such as data entry, follow-ups, and document generation. This saves time and resources, allowing staff to focus on high-value activities and providing better customer service.
🌟 Integration Capabilities:
CRM software can integrate with other essential systems used by financial institutions, such as accounting software, portfolio management tools, and customer support platforms. This facilitates seamless data flow and ensures a unified view of customer interactions across departments.
Enhanced Customer Engagement
CRM software plays a crucial role in enhancing customer engagement for financial institutions. By utilizing multiple communication channels, such as phone calls, emails, social media, and live chats, CRM software enables institutions to interact with customers seamlessly. This allows for personalized and timely interactions, making customers feel valued and heard at every touchpoint. The ability to engage customers across various channels also ensures convenience and flexibility, as customers can choose their preferred method of communication.
Furthermore, CRM software enables financial institutions to track and monitor customer interactions effectively. Each interaction is recorded within the CRM system, providing a comprehensive history of customer engagements. This information can be utilized by financial institutions to gain insights into customer preferences, needs, and behaviors. By understanding customers better, institutions can tailor their offerings and communication strategies, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Additionally, CRM software facilitates the management of customer inquiries and support requests. Through integrated ticketing systems and automated workflows, institutions can efficiently handle and resolve customer issues. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also helps build trust and long-term relationships. CRM software ensures that customer inquiries are addressed promptly and consistently, creating a positive customer experience.
Overall, enhanced customer engagement is a significant strength of financial services CRM software. By utilizing various communication channels, tracking interactions, and providing efficient customer support, financial institutions can build strong relationships with their customers and differentiate themselves in a competitive market.
Data Centralization
One of the key strengths of CRM software is its ability to centralize customer data. In a financial services context, customer data is scattered across various systems and departments, making it challenging to gain a complete view of each customer. CRM software addresses this challenge by consolidating all customer-related information into a single database.
By centralizing customer data, financial institutions can access a comprehensive and holistic view of each customer. This view includes contact details, transaction history, communication records, preferences, and any other relevant information. Having all this information readily available empowers institutions to provide personalized experiences and targeted marketing efforts. For example, if a customer has recently expressed interest in a specific financial product, institutions can leverage this information to deliver tailored offers and recommendations.
Moreover, centralizing customer data enables financial institutions to gain valuable insights into customer behaviors and patterns. By analyzing the data, institutions can identify trends, segment customers based on demographics or preferences, and make data-driven decisions. This information can be used to develop marketing strategies, improve sales processes, and enhance overall customer experience.
Another advantage of data centralization is the elimination of data silos and duplication. With CRM software, information is entered and updated in one central location, reducing the chances of data discrepancies or conflicting records. This ensures data accuracy and integrity, allowing financial institutions to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
In summary, data centralization is a significant strength of financial services CRM software. By consolidating customer data into a single database, institutions can access a holistic view of customers, gain valuable insights, and provide personalized experiences that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Streamlined Sales Process
A streamlined sales process is crucial for financial institutions to drive revenue generation and business growth. CRM software offers a range of tools and features that help automate and optimize the sales process, making it more efficient and effective.
One of the key strengths of CRM software in streamlining the sales process is lead management. CRM software allows financial institutions to track and manage leads from initial contact to conversion. Leads can be captured through various channels, such as website forms, social media, or marketing campaigns, and seamlessly integrated into the CRM system. Once captured, leads can be assigned to sales representatives based on predefined criteria, ensuring efficient lead distribution.
CRM software also facilitates lead nurturing and engagement. By utilizing automated workflows and personalized communication, institutions can keep leads engaged throughout the buyer's journey. This includes sending targeted emails, scheduling follow-up calls, or providing relevant content based on the lead's interests and preferences. By nurturing leads effectively, financial institutions can increase the chances of conversion and shorten the sales cycle.
In addition to lead management, CRM software provides features for tracking and managing the sales pipeline. Financial institutions can easily monitor the progress of each opportunity, from initial contact to deal closure. This allows sales teams to prioritize and focus on high-potential opportunities, ensuring efficient resource allocation and maximizing revenue generation.
CRM software also offers features for task and activity management. Sales representatives can create tasks, schedule follow-ups, and set reminders within the CRM system. This ensures that important actions are not missed and that the sales process moves smoothly. Automated notifications and alerts can be set up to keep sales representatives informed about upcoming tasks or deadlines, improving efficiency and productivity.
Furthermore, CRM software provides real-time visibility into sales performance through customizable dashboards and reports. Financial institutions can track key performance metrics, such as revenue generated, conversion rates, and average deal size. This information allows sales managers to identify bottlenecks, analyze performance trends, and make data-driven decisions to optimize the sales process.
In summary, CRM software streamlines the sales process for financial institutions by offering lead management, lead nurturing, pipeline tracking, task management, and performance analytics. By leveraging these features, institutions can enhance sales team productivity, improve conversion rates, and drive revenue growth.
Customizable Dashboards and Reports
Customizable dashboards and reports are key features of financial services CRM software that provide real-time insights into key performance metrics. These features enable financial institutions to monitor and evaluate various aspects of their operations, allowing for data-driven decision-making and performance evaluation.
CRM software offers customizable dashboards that provide a visual representation of important metrics, such as sales performance, customer satisfaction levels, andmarketing campaign outcomes. Financial institutions can customize these dashboards to display the specific metrics and data points that are most relevant to their business objectives. For example, a sales manager may choose to display the number of leads generated, conversion rates, and revenue generated by each sales representative on their dashboard. This allows for a quick and easy overview of performance and helps identify areas that require attention or improvement.
In addition to customizable dashboards, CRM software also provides the ability to generate detailed reports. These reports can be customized to include specific data points, timeframes, and filters. Financial institutions can create reports that provide insights into customer behavior, sales trends, marketing campaign effectiveness, and more. These reports can be used for performance evaluation, strategic planning, and identifying areas for growth and improvement.
The availability of real-time data through customizable dashboards and reports allows financial institutions to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. For example, a marketing manager can analyze the response rates of different marketing campaigns and adjust strategies accordingly. Sales managers can identify bottlenecks in the sales process and allocate resources effectively. Executives can monitor overall business performance and make strategic decisions to drive growth.
Furthermore, CRM software often provides the ability to schedule and automate the generation of reports. This ensures that key stakeholders receive the necessary information on a regular basis without manual effort. Scheduled reports can be delivered via email or accessed directly within the CRM system, providing convenience and ensuring that decision-makers have the information they need when they need it.
Overall, customizable dashboards and reports are powerful features of financial services CRM software that enable financial institutions to monitor performance, gain insights, and make data-driven decisions. By leveraging these features effectively, institutions can optimize their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
Weaknesses of Financial Services CRM Software
🔴 Complexity and Learning Curve:
Implementing and configuring CRM software can be complex, requiring significant time and effort. Financial institutions need to invest resources in understanding the software, setting up the system, and training employees on its usage. Additionally, employees may initially find it challenging to adapt to the new system and fully utilize its capabilities, leading to a learning curve and potential productivity dips during the transition period.
🔴 Cost:
Acquiring and implementing CRM software can involve substantial costs, including licensing fees, customization expenses, and ongoing maintenance charges. Financial institutions must carefully evaluate the return on investment and long-term benefits before committing to a CRM solution. It is essential to consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation costs, training expenses, and any additional integrations or customizations required.
🔴 Data Quality and Accuracy:
CRM software heavily relies on accurate and up-to-date data to deliver meaningful insights and personalized experiences. Inaccurate or incomplete data can compromise the effectiveness of the software, making data management and cleansing essential for optimal performance. Financial institutions need to ensure that data entry processes are standardized, accurate, and regularly audited to maintain data integrity.
🔴 Resistance to Change:
Introducing CRM software may face resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing processes or fear job displacement due to automation. Effective change management strategies, training programs, and clear communication are crucial to address such concerns and ensure successful adoption. It is important to involve employees in the decision-making process, provide training and support, and highlight the benefits of the CRM software to alleviate resistance.
🔴 Integration Challenges:
Integrating CRM software with existing legacy systems or third-party applications can pose technical challenges. Financial institutions must assess the compatibility and scalability of their current infrastructure to ensure a smooth integration process. Depending on the complexity of the existing systems, additional resources and expertise may be required to establish seamless data flow and integration between systems.
🔴 Cybersecurity Risks:
As CRM software deals with sensitive customer data, it becomes a potential target for cyberattacks. Financial institutions must implement robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular vulnerability assessments, to protect customer information from unauthorized access or breaches. Regular security audits and employee training on cybersecurity best practices are crucial to minimize the risk of data breaches.
🔴 Dependency on User Input:
CRM software relies on accurate and timely input from users to maintain data integrity and deliver accurate insights. Inadequate user training or negligence can result in incomplete or incorrect data, compromising the effectiveness of the software. Financial institutions need to provide comprehensive training programs and establish data management protocols to ensure that users understand the importance of accurate data entry and adhere to best practices.
🔴 Scalability:
As financial institutions grow and expand their operations, the scalability of CRM software becomes a consideration. CRM software should be capable of handling increasing volumes of customer data, user accounts, and system integrations without compromising performance. Financial institutions need to evaluate the scalability of the CRM software and ensure that it can accommodate future growth and evolving business needs.
Complexity and Learning Curve
The implementation and configuration of CRM software can be complex, requiring careful planning and investment of resources. Financial institutions need to allocate time and effort to understand the software's functionalities, set up the system to align with their specific business processes, and train employees on how to effectively use the software.
During the implementation phase, financial institutions should conduct a thorough analysis of their existing processes and workflows to determine how the CRM software can be integrated. This may involve mapping out current systems, data flows, and customer touchpoints. Understanding the various integration points and dependencies will help ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
Once the CRM software is implemented, there may be a learning curve for employees who are accustomed to the previous systems or manual processes. Training programs should be designed to address this learning curve and provide comprehensive guidance on how to use the CRM software effectively. This includes training sessions, user guides, and ongoing support to address any questions or challenges that may arise.
To ease the transition and encourage adoption, financial institutions can appoint internal champions or super-users who are proficient in using the CRM software. These individuals can provide guidance and support to their colleagues, helping them navigate the system and leverage its capabilities. Regular feedback loops and communication channels should be established to address user concerns and continuously improve the user experience.
It is important to remember that the complexity and learning curve associated with CRM software implementation are temporary challenges. Once employees become familiar with the system and its benefits become apparent, the software can significantly enhance their productivity and effectiveness in managing customer relationships.
Cost
Acquiring and implementing CRM software involves costs that financial institutions need to carefully consider and evaluate. These costs can include licensing fees, customization expenses, training programs, ongoing maintenance charges, and potential costs associated with system integrations.
Financial institutions should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis to assess the return on investment (ROI) of implementing CRM software. This analysis should consider both the immediate and long-term benefits that the CRM software can bring to the organization. Factors to consider include improved sales performance, enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty, increased operational efficiency, and the potential for revenue growth.
When evaluating the cost of CRM software, financial institutions should also consider the total cost of ownership (TCO). This includes not only the upfront costs but also the ongoing expenses associated with maintenance, updates, and any required integrations. Additionally, the scalability of the CRM software should be evaluated to ensure that it can accommodate the future growth and evolving needs of the organization without significant additional costs.
Financial institutions may also explore different pricing models offered by CRM software vendors. Some vendors offer flexible pricing options, such as subscription-based models or pay-per-user plans, which can be more cost-effective for smaller institutions or those with fluctuating user requirements. It is important to negotiate and clarify pricing details with the vendor to avoid any unexpected expenses.
Ultimately, financial institutions need to weigh the costs against the expected benefits and choose a CRM software solution that aligns with their budget and business goals. A well-planned implementation strategy, along with ongoing monitoring and optimization, can help maximize the value and ROI of CRM software.
Data Quality and Accuracy
Data is the lifeblood of CRM software, and its quality and accuracy are essential for optimal performance. Financial institutions must ensure that the data entered into the CRM system is complete, accurate, and up-to-date. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed insights, misinformed decision-making, and compromised customer interactions.
To maintain data integrity, financial institutions need to establish data management protocols and best practices. This includes defining data entry standards, implementing validation rules, and enforcing data cleansing processes. Regular audits should be conducted to identify and rectify any data quality issues, such as duplicate records or outdated information.
Financial institutions can also leverage data validation tools and automated processes to ensure that data entered into the CRM system meets predefined criteria. These tools can help flag potential errors or inconsistencies in real-time, ensuring that only accurate and reliable data is captured. Additionally, data governance policies should be established to determine who has access to the CRM system and who is responsible for maintaining data accuracy.
Employee training and awareness programs are crucial for maintaining data quality. Employees should be educated on the importance of accurate data entry, the potential consequences of data errors, and the role they play in ensuring data accuracy. Ongoing training and performance monitoring can help reinforce good data management practices and empower employees to take ownership of data quality.
Regular data audits and quality checks should be conducted to identify any patterns or trends in data errors. This information can be used to identify areas for improvement, provideadditional training or support to employees, and refine data management processes.
Furthermore, financial institutions can leverage data integration and data cleansing tools to improve data quality. These tools can help consolidate data from various sources, identify and merge duplicate records, and validate data against predefined criteria. Regular data cleansing exercises should be conducted to remove outdated or irrelevant information, ensuring that the CRM system remains a reliable source of customer data.
It is important to note that maintaining data quality and accuracy is an ongoing process. As customer data evolves and new information is collected, financial institutions must continuously monitor and update the data within the CRM system. By prioritizing data quality and accuracy, financial institutions can leverage the full potential of CRM software and make informed decisions based on reliable and meaningful data.
Resistance to Change
Introducing CRM software into an organization can face resistance from employees who are accustomed to existing processes or fear job displacement due to automation. It is essential to address these concerns and foster a culture of change and adoption within the organization.
One of the key strategies to overcome resistance to change is effective communication. Financial institutions should clearly communicate the reasons for implementing CRM software, the benefits it brings to the organization, and how it aligns with the overall business strategy. Transparent communication helps employees understand the purpose and value of the CRM software, alleviating any fears or misconceptions they may have.
Employees should be involved in the decision-making process whenever possible. By seeking their input and feedback, financial institutions can address concerns, gain buy-in, and ensure that the CRM software meets the needs of the end-users. Involving employees also creates a sense of ownership and empowerment, making them more receptive to the changes brought about by the CRM software.
Training and support programs are crucial for successful adoption. Financial institutions should invest in comprehensive training programs that equip employees with the knowledge and skills to effectively use the CRM software. The training should be tailored to different user roles and should focus on the specific functionalities and benefits that are relevant to each role. Ongoing support should also be provided, with dedicated resources available to address any questions or challenges that arise during the adoption process.
It is important to highlight the benefits of the CRM software to employees. Emphasize how it can streamline their workflows, improve productivity, and enhance their ability to serve customers. By showcasing the positive impact of the CRM software on individual job roles, financial institutions can alleviate concerns and build enthusiasm among employees.
Recognizing and celebrating success stories and early adopters can also help drive adoption. By highlighting the achievements and positive outcomes resulting from using the CRM software, financial institutions can create a sense of excitement and motivation among employees. This can encourage others to embrace the change and see the CRM software as a valuable tool rather than a threat to their roles.
Overall, overcoming resistance to change requires clear communication, employee involvement, comprehensive training, ongoing support, and a focus on the benefits and positive impact of the CRM software. By addressing concerns and fostering a culture of adoption, financial institutions can successfully implement CRM software and unlock its full potential.
Integration Challenges
Integrating CRM software with existing legacy systems or third-party applications can present technical challenges that financial institutions need to address during the implementation process. The success of the integration largely depends on the compatibility and scalability of the existing infrastructure.
Prior to implementing CRM software, financial institutions should conduct a thorough assessment of their current systems and identify potential integration points. This includes understanding the data flow between systems, identifying any dependencies or limitations, and determining the feasibility of integrating the CRM software with existing systems.
Financial institutions should work closely with the CRM software vendor and their IT teams to ensure a smooth integration process. The vendor should provide documentation and guidance on the integration process, including any APIs or connectors available. It is essential to establish clear communication channels and have regular meetings to address any technical challenges or questions that may arise during the integration process.
Depending on the complexity of the existing systems, financial institutions may need to allocate additional resources or expertise to manage the integration. This may involve engaging third-party consultants or developers who specialize in system integration. These experts can help identify potential bottlenecks, develop custom integration solutions, and ensure that data flows seamlessly between systems.
Testing and validation are crucial steps in the integration process. Financial institutions should conduct thorough testing to ensure that data is accurately transferred between systems, that there are no data inconsistencies or data loss, and that the integrated systems function as expected. This may involve running test scenarios, performing data validation checks, and engaging end-users to validate the integration from their perspective.
It is important to note that integrating CRM software with existing systems is not a one-time event. Financial institutions should regularly review and assess the integration to ensure that it remains effective as the business evolves. As new systems or applications are introduced, the integration may need to be modified or expanded to accommodate the changing needs of the organization.
Cybersecurity Risks
As CRM software deals with sensitive customer data, it becomes a potential target for cyberattacks. Financial institutions must prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect customer information and maintain trust.
One of the key cybersecurity measures is data encryption. Financial institutions should ensure that data transmitted between the CRM software and other systems is encrypted using secure protocols. This prevents unauthorized access or interception of sensitive information. Data at rest should also be encrypted to protect against potential breaches or unauthorized access to the CRM system's database.
Access controls are essential to limit access to the CRM software and ensure that only authorized individuals can view or modify customer data. Financial institutions should implement user authentication mechanisms, such as strong passwords, two-factor authentication, or biometric authentication, to prevent unauthorized access to the CRM system. Role-based access controls should be established to grant appropriate privileges to different user roles within the organization.
Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address any weaknesses or vulnerabilities in the CRM software or the overall infrastructure. This involves engaging third-party security experts who can simulate cyberattacks and identify potential entry points or vulnerabilities. The findings from these assessments should be used to implement necessary security patches or updates.
Employee training and awareness programs play a crucial role in preventing cybersecurity breaches. Financial institutions should educate employees on best practices for data security, such as identifying phishing attempts, avoiding suspicious links or attachments, and maintaining strong password hygiene. Employees should be trained to recognize and report potential security incidents promptly.
Regular monitoring and auditing of the CRM system's security logs and access logs are essential to detect any suspicious activities or potential breaches. Financial institutions should establish incident response protocols to address security incidents promptly and effectively. This includes having a designated incident response team, defining communication channels, and conducting post-incident analysis to identify any areas for improvement.
Compliance with industry regulations is also crucial for maintaining cybersecurity in financial services. Financial institutions should ensure that their CRM software meets all relevant regulatory requirements, such as data privacy laws or financial industry regulations. This includes implementing mechanisms for data retention, data deletion, and providing audit trails for regulatory purposes.
By implementing robust cybersecurity measures, financial institutions can protect customer data, maintain trust, and mitigate the risks associated with CRM software usage.
Dependency on User Input
CRM software relies on accurate and timely input from users to maintain data integrity and deliver accurate insights. Inadequate user training or negligence can result in incomplete or incorrect data, compromising the effectiveness of the software. Financial institutions must prioritize user training and establish data management protocols to mitigate this weakness.
Comprehensive user training programs should be put in place to ensure that employees understand the importance of accurate data entry and how to effectively utilize the CRM software. Training sessions should cover data entry best practices, data validation rules, and the implications of inaccurate or incomplete data. Hands-on exercises and simulations can be used to reinforce learning and allow users to practice data entry within a controlled environment.
Data management protocols should be established to guide users on data entry standards and processes. This includes defining data fields, establishing data validation rules, and implementing data cleansing procedures. Financial institutions should provide clear guidelines on how to handle common data entry scenarios and address any potential data quality issues.
Regular data audits should be conducted to identify any patterns or trends in data errors. This information can help identify areas for improvement and provide targeted training or support to users who may require additional guidance. Financial institutions should also establish performance metrics and goals related to data quality, and monitor and assess user performance regularly.
Automated processes and system validations can be implemented to minimize the dependency on user input and improve data accuracy. For example, CRM software can be configured to enforce mandatory fields or perform real-time validation checks to ensure that critical data is entered accurately. Workflow automation can also be utilized to streamline data entry processes and reduce the chances of errors caused by manual input.
Ultimately, financial institutions need to emphasize the importance of accurate data entry and provide ongoing support and training to users. By establishing data management protocols, leveraging automated processes, and continuously monitoring data quality, financial institutions can mitigate the dependency on user input and ensure that the CRM software operates effectively.
Financial Services CRM Software: Features and Functionality
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Lead Management | Track and manage leads from initial contact to conversion. Capture lead information, assign leads to sales representatives, and track the progress of each lead through the sales pipeline. |
| Contact Management | Store and organize customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers,and email addresses. Keep track of customer preferences, communication history, and any other relevant details. |
| Sales Pipeline Management | Monitor and track sales opportunities through various stages, from initial contact to deal closure. View the status of each opportunity, track interactions, and forecast revenue. |
| Customer Segmentation | Segment customers based on demographics, behaviors, and preferences. Group customers into specific categories to tailor marketing efforts, personalized communication, and targeted campaigns. |
| Interaction Tracking | Record and analyze customer interactions across channels, such as phone calls, emails, meetings, or social media interactions. Keep a comprehensive history of customer engagements to understand their preferences and needs. |
| Task and Activity Management | Assign and track tasks and activities for individuals or teams. Set reminders, deadlines, and priorities to ensure timely follow-ups and completion of tasks. |
| Reporting and Analytics | Generate reports and gain insights into key performance metrics. Analyze sales performance, customer satisfaction levels, marketing campaign effectiveness, and other relevant data to make data-driven decisions. |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the key benefits of using financial services CRM software?
Financial services CRM software provides several benefits, including enhanced customer engagement, streamlined sales processes, personalized marketing campaigns, improved data-driven decision-making, increased operational efficiency, and improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Is financial services CRM software suitable for small-scale financial institutions?
Yes, financial services CRM software can benefit organizations of all sizes, including small-scale financial institutions. The software can help streamline operations, improve customer relationships, and compete effectively in the market, regardless of the organization's size.
3. Can financial services CRM software integrate with existing systems?
Yes, CRM software offers integration capabilities to seamlessly connect with existing systems, such as accounting software, portfolio management tools, and customer support platforms. This ensures a unified view of customer interactions and improves operational efficiency.
4. How can CRM software help in compliance management?
CRM software ensures compliance with industry regulations by providing audit trails, data encryption, access controls, and other security features. It helps financial institutions meet regulatory requirements and maintain customer trust.
5. What challenges can arise during the implementation of financial services CRM software?
Common challenges during CRM software implementation include complexity and a learning curve associated with the software, cost considerations, data quality and accuracy, resistance to change from employees, integration complexities with existing systems, cybersecurity risks, and dependency on user input for accurate data entry.
6. Can financial services CRM software be customized to specific business needs?
Yes, CRM software can be customized to align with specific business requirements. Organizations can tailor the software's features, workflows, and user interfaces to suit their unique processes and objectives.
7. How much does financial services CRM software typically cost?
The cost of CRM software varies depending on factors such as the vendor, deployment model (cloud-based or on-premises), number of users, and required customization. It is important to evaluate the total cost of ownership and the expected return on investment before making a purchase decision.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial services CRM software is a powerful tool that revolutionizes customer relationship management in the financial industry. It offers a range of benefits, including enhanced customer engagement, streamlined sales processes, personalized interactions, and improved data-driven decision-making. However, financial institutions must also be aware of the potential challenges associated with CRM software, such as complexity, cost considerations, data quality, resistance to change, integration complexities, cybersecurity risks, and dependency on user input.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of financial services CRM software and implementing proper strategies to address the challenges, financial institutions can leverage CRM software to enhance customer relationships, drive business growth, and gain a competitive edge in the market. It is important to carefully evaluate different CRM software options, customize the software to align with specific business needs, provide comprehensive training and support to employees, and continuously monitor and optimize the CRM system to maximize its effectiveness.
Financial services CRM software has become an indispensable tool for financial institutions in managing customer relationships effectively. By utilizing the features and functionalities of CRM software, financial institutions can build strong customer relationships, improve operational efficiency, and drive business growth. It is essential for financial institutions to choose the right CRM software solution, invest in proper implementation and training, and continuously adapt and optimize the CRM system to meet the evolving needs of the organization.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for informational purposes only. The use of financial services CRM software should be based on thorough research and evaluation of the specific needs and requirements of your organization.
Post a Comment
Post a Comment